Are you a pet owner or a dog lover? Would you like to learn more about their behavior? Grasping the intricacies of your pets is essential for their proper care and management. Whether you have a canine companion, work with pets professionally, or simply wish to expand your knowledge, this article will provide comprehensive insights.

Dogs are captivating creatures with distinct personalities and behaviors. They interact with one another, establish social hierarchies, and adapt to their surroundings. Understanding dog behavior is pivotal for pet owners, dog trainers, and those who cherish them. This guide will delve into the fundamental aspects of their behavior, encompassing communication, aggression, reproduction, and social conduct.
%20(2)-2.jpg)
The Significance of Comprehending Dog Behavior
Essential knowledge of dog behavior serves several purposes. Firstly, it is crucial for their proper care and management. For instance, recognizing your dog's communication cues can help identify moments of stress or discomfort. Additionally, comprehension of dog behavior is critical for animal trainers and behaviorists engaged in professional pet care. Proficiency in behavior modification techniques can enhance the overall well-being of animals.
-1.jpg)
Communication
Communication stands as a vital facet of animal behavior. Animals employ diverse methods of communication, including vocalizations, body language, and scent marking. Different animals utilize distinct communication modes, underscoring the importance of interpreting these signals accurately.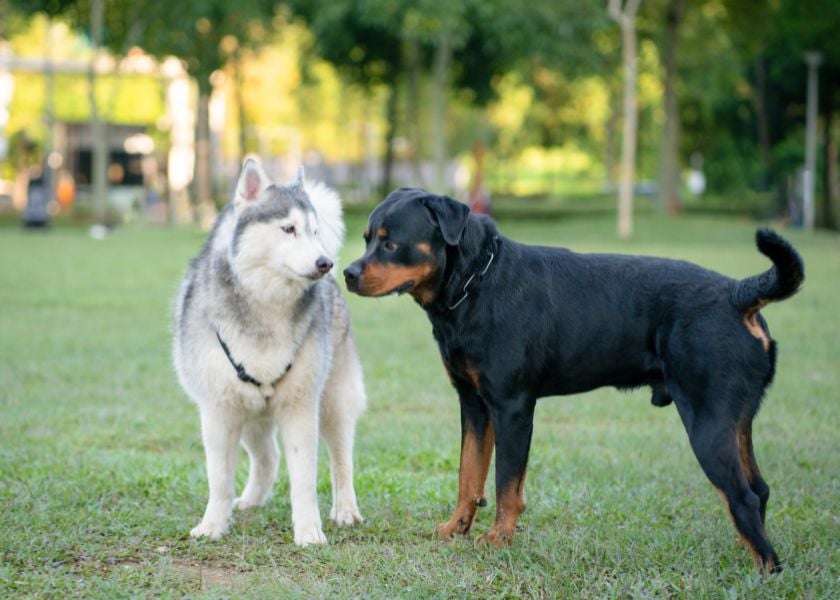
- Vocalizations:
Pets employ vocalizations to communicate with one another. These auditory signals can be simple or intricate, conveying various messages. For instance, dogs employ barks, growls, and whines to express emotions like excitement, fear, or aggression. Cats, on the other hand, use meows, purrs, and hisses to convey their needs and emotions. - Body Language:
Another pivotal communication avenue for dogs is body language. Through their postures and movements, dogs convey emotions, assert dominance, and express intent. A wagging tail signifies excitement or happiness, while an elevated tail and tall stance indicate dominance. Proficiency in interpreting your pet's body language fosters a deeper connection and better comprehension of their behavior.
- Scent Marking:
Dogs employ scent marking to communicate through their distinct odors. This can involve urine, feces, or glandular secretions to mark territory, attract mates, or signal warnings. Recognizing scent marking aids pet owners in identifying territorial behavior and stress indicators in their pets.
Aggression
While often perceived negatively, aggression is a natural behavior animals utilize to assert dominance, safeguard territory, and defend themselves. However, unchecked aggression can be hazardous and detrimental, underlining the need to discern various aggression types.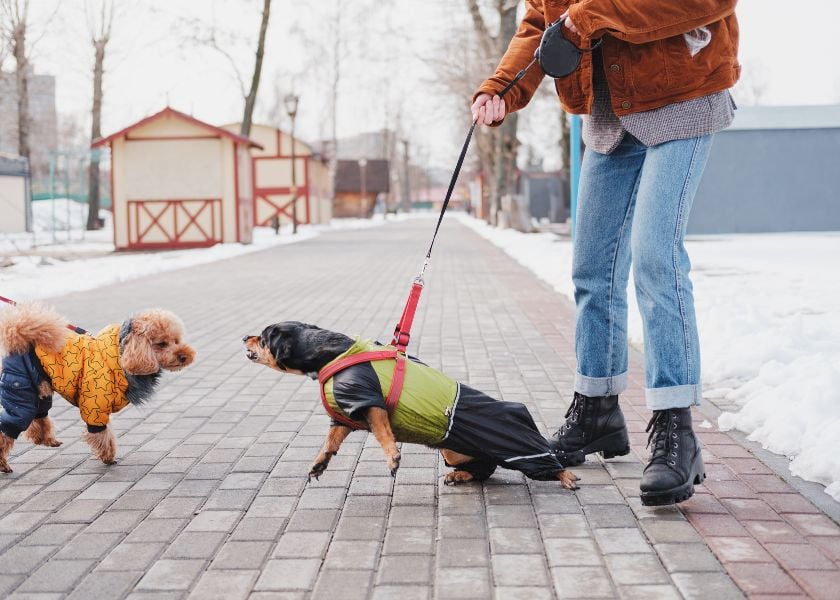
- Territorial Aggression: Dogs showcase territorial aggression to protect their domain from intruders. Barking and growling serve as warnings to trespassers entering their territory.
- Fear Aggression: When feeling threatened or scared, pets resort to fear aggression.
- Dominance Aggression: Dogs display dominance aggression to establish dominance over others, even extending to their owners.
- Social Aggression: To establish their social hierarchy, dogs employ social aggression.
- Redirected Aggression: This type occurs when pets can't direct aggression at the source of conflict.
Understanding these diverse aggression types aids pet owners and trainers in managing aggressive behavior, mitigating potential harm.
Reproduction
Reproduction is another essential aspect of animal behavior. Animals use various methods to attract mates and reproduce, such as courtship behaviors and mating rituals. 
- Courtship Behaviors: Dogs utilize courtship behaviors to attract mates, which can involve vocalizations, displays of strength, or visual exhibitions.
- Mating Rituals: Preceding and during mating, dogs engage in a series of behaviors termed mating rituals.
A grasp of animals' reproductive behaviors assists pet owners and professionals in managing breeding initiatives and enhancing captive animal welfare.
Social Behavior
Social behavior represents a pivotal aspect of dog behavior. Dogs, being social creatures, employ diverse methods to forge social bonds and relationships.
- Social Bonds: Dogs establish relationships with one another, driven by factors like kinship or mutual benefit.
- Group Dynamics: Interactions among group members constitute group dynamics. Dogs use varied approaches to establish social hierarchies, including aggression and submission. This understanding proves vital for managing group-housed animals.
Dog Behavior Essentials: What You Need to Know
To summarize, understanding dog behavior essentials is paramount for proper dog care and management. Ranging from communication to aggression, reproduction to social conduct, various aspects of dog behavior merit comprehension. Through this understanding, pet owners and trainers contribute to animal welfare enhancement and protection of endangered species.